Product Description
Product Description
| Product Name | 626 Auto Parts Car Steering System Accessories Power steeing Gear Box Rack And Pinion |
| Application | 626 Automoile Steering system |
| OEM NO | GA2A-32-110N |
| Car Make | 626 |
| Warranty | 12 Months |
| Weight | 11KG |
| Drive Xihu (West Lake) Dis. | LHD |
| Type | HYDRAULIC |
| ZUA NO | F-MZ-007 |
Our Advantages
Company Profile
Exhibition
| After-sales Service: | 24-Hour on-Line |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 12 Months |
| Type: | Steering Rack |
| Material: | Metal and Plastic |
| Certification: | ISO, IATF16949 |
| Automatic: | EPS |
| Samples: |
US$ 499/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
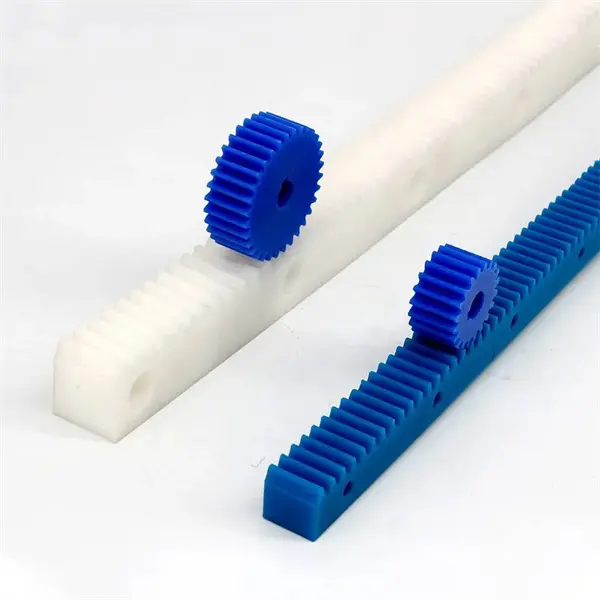

How do rack and pinion systems handle different gear ratios?
Rack and pinion systems are capable of accommodating different gear ratios to achieve specific mechanical advantages and motion characteristics. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rack and pinion systems handle different gear ratios:
In a rack and pinion system, the gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the pinion gear and the length of the rack. The gear ratio defines the relationship between the rotational motion of the pinion and the linear motion of the rack. Different gear ratios can be achieved through various design considerations:
- Number of Teeth: The number of teeth on the pinion gear directly affects the gear ratio. A larger number of teeth on the pinion gear compared to the number of rack teeth results in a higher gear ratio, providing increased mechanical advantage and slower linear motion of the rack per revolution of the pinion. Conversely, a smaller number of pinion teeth relative to the rack teeth yields a lower gear ratio, delivering higher linear speed but reduced mechanical advantage.
- Pitch Diameter: The pitch diameter of the pinion gear, which is the diameter of the imaginary circle formed by the gear teeth, also influences the gear ratio. Increasing the pitch diameter of the pinion relative to the rack diameter leads to a higher gear ratio, while decreasing the pitch diameter results in a lower gear ratio. By adjusting the pitch diameters of the pinion and rack, different gear ratios can be achieved.
- Module or Diametral Pitch: The module (for metric systems) or diametral pitch (for inch systems) is a parameter that defines the size and spacing of the teeth on the gear. By selecting different module or diametral pitch values, the gear ratio can be adjusted. A larger module or lower diametral pitch leads to a lower gear ratio, while a smaller module or higher diametral pitch results in a higher gear ratio.
- Multiple Stages: Rack and pinion systems can also incorporate multiple stages of gears to achieve complex gear ratios. By combining multiple pinion gears and racks, each with different tooth counts, gear ratios can be multiplied or divided to achieve the desired overall gear ratio. This approach allows for more flexibility in achieving specific motion requirements and torque transmission characteristics.
When selecting the appropriate gear ratio for a rack and pinion system, several factors should be considered, such as the desired linear speed, torque requirements, precision, and system constraints. Higher gear ratios provide increased mechanical advantage and torque multiplication, which is advantageous for applications requiring heavy loads or precise motion control. Lower gear ratios, on the other hand, offer higher linear speed and reduced mechanical advantage, suitable for applications that prioritize rapid movements.
It’s important to note that changing the gear ratio in a rack and pinion system may impact other performance aspects, such as backlash, load distribution, and system efficiency. Proper design considerations, tooth profile selection, and material choices should be made to ensure optimal performance and reliability while maintaining the desired gear ratio.
Can rack and pinion systems be integrated into robotic and automation equipment?
Yes, rack and pinion systems can be successfully integrated into robotic and automation equipment to facilitate precise and efficient motion control. Here’s a detailed explanation of how rack and pinion systems can be utilized in robotic and automation applications:
Rack and pinion systems offer several advantages that make them well-suited for integration into robotic and automation equipment:
- Precision and Accuracy: Rack and pinion systems provide high precision and accuracy in motion control. The direct engagement between the pinion and the rack ensures a positive and backlash-free transfer of motion, allowing for precise positioning and repeatability. This characteristic is essential in robotic and automation applications that require accurate movement and positioning of components.
- High Speed and Acceleration: Rack and pinion systems are capable of operating at high speeds and accommodating rapid accelerations. The direct power transmission and efficient torque transfer of rack and pinion mechanisms enable quick and dynamic movements, making them suitable for applications that demand fast and agile robotic motions.
- Compact Design: Rack and pinion systems offer a compact design, which is advantageous in space-constrained robotic and automation setups. The linear nature of the rack allows for efficient integration into robotic arms, linear stages, and other motion control systems. This compact design maximizes the workspace utilization and allows for flexible placement of the rack and pinion mechanism.
- High Load Capacity: Rack and pinion systems can handle substantial loads while maintaining efficient power transmission. The engagement of the teeth provides a large contact area, allowing for the effective distribution of forces and torque. This characteristic is essential for robotic and automation equipment that needs to manipulate heavy payloads or exert significant forces.
- Versatility: Rack and pinion systems offer versatility in terms of design options and configuration possibilities. They can be implemented in various orientations, such as horizontal, vertical, or inclined setups, to accommodate different robotic and automation requirements. Additionally, rack and pinion systems can be combined with other mechanisms, such as gears and belts, to achieve complex motion profiles and multi-axis control.
- Reliability and Durability: Rack and pinion systems are known for their durability and long service life. When properly designed and maintained, they can withstand high loads, repetitive movements, and demanding operating conditions. This reliability is crucial in robotic and automation equipment, where continuous and uninterrupted operation is essential.
Overall, the integration of rack and pinion systems in robotic and automation equipment offers precise motion control, high-speed capability, compactness, load-handling capabilities, versatility, and reliability. These characteristics make rack and pinion systems a popular choice in applications such as pick-and-place robots, CNC machines, packaging equipment, material handling systems, and assembly lines.

Can you explain the typical applications of rack and pinion systems?
Rack and pinion systems find a wide range of applications in various industries due to their versatility, efficiency, and precise motion control. Here’s a detailed explanation of some typical applications:
- Automotive Steering: One of the most common applications of rack and pinion systems is in automotive steering mechanisms. In this application, the rack is connected to the steering column, and the pinion gear is driven by the steering input from the driver. As the pinion gear rotates, it moves the rack linearly, which in turn controls the movement of the vehicle’s front wheels, allowing for smooth and responsive steering.
- Robotics: Rack and pinion systems are widely used in robotics for precise and controlled linear motion. They can be found in various robotic applications, including robotic arms, gantry systems, pick-and-place robots, and CNC machines. The rack and pinion mechanism enables accurate positioning, fast movement, and high repeatability, making it ideal for tasks that require precise manipulation and motion control.
- Linear Actuators: Rack and pinion systems are commonly employed in linear actuators, which are devices used to convert rotational motion into linear motion. The pinion gear is driven by an electric or hydraulic motor, and the linear motion of the rack is utilized to extend or retract the actuator. Linear actuators based on rack and pinion systems are used in various applications, such as industrial automation, medical equipment, and aerospace systems.
- Machinery: Rack and pinion systems are utilized in a wide range of machinery and equipment. They are often employed in applications requiring precise linear motion control, such as cutting machines, printing presses, packaging equipment, and material handling systems. The rack and pinion mechanism enables efficient power transmission, accurate positioning, and quick response, enhancing the performance and productivity of the machinery.
- Automation: Rack and pinion systems play a crucial role in automation processes. They are used in automated systems for tasks such as part positioning, assembly, sorting, and conveyor systems. The precise and reliable linear motion provided by rack and pinion systems contributes to the efficiency and accuracy of automated processes.
In addition to the above applications, rack and pinion systems can be found in various other fields, including agriculture, construction, entertainment industry, and more. Their compact design, high precision, efficiency, and versatility make them a popular choice for converting rotational motion into linear motion in a wide range of mechanical systems.


editor by CX 2023-10-08